Histone 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Analysis Service
Based on high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms and specific peptide enrichment technologies, MtoZ Biolabs has launched histone 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation analysis service to systematically detect and quantitatively analyze histone 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation modifications. This service enables precise identification of modification sites in complex samples and captures their abundance changes. Combined with multidimensional bioinformatics methods, it outputs high-quality data, including modification site distribution, quantitative differences, and functional annotation. This helps researchers comprehensively analyze the regulatory features of histone Khib modifications and their roles in gene expression and epigenetics research, providing solid data support for functional mechanism studies and potential biomarker discovery.
Overview
Histone 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation (Khib) is a newly identified important lysine post-translational modification characterized by the covalent attachment of a 2-hydroxyisobutyryl group to histone lysine residues, thereby altering chromatin structure and regulating gene expression. Khib plays key roles in various biological processes, especially in chromatin remodeling, DNA repair, metabolic regulation, and the expression of reproduction-related genes. Histone 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation analysis allows systematic detection and quantitative profiling, accurately revealing its site distribution, abundance changes, and functional associations. It is widely applied in epigenetics research, cell signaling pathway analysis, disease mechanism exploration, and potential biomarker discovery, providing reliable data support for a deeper understanding of the mechanisms by which Khib functions in life activities.
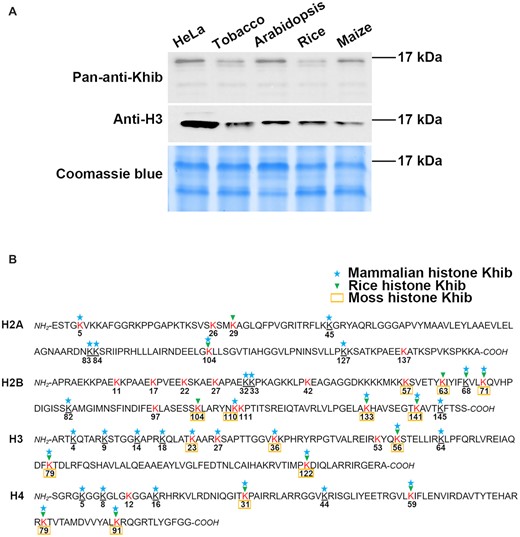
Zheng, L L. et al. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021.
Figure 1. Identification of Arabidopsis Histone Lysine 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Modifications.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation and Protein Extraction
Protein extraction and preprocessing of cell or tissue samples are performed to ensure the integrity and stability of the modifications.
2. Proteolysis and Peptide Enrichment
Enzymatic digestion is carried out under optimized conditions, and specific enrichment strategies are applied to capture 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation–modified peptides.
3. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Detection
Relying on advanced LC-MS/MS platforms, precise identification and quantitative analysis of modification sites are achieved.
4. Data Analysis and Functional Annotation
Through database searching and bioinformatics methods, results include modification site distribution, abundance changes, and functional annotations, generating a systematic modification profile.
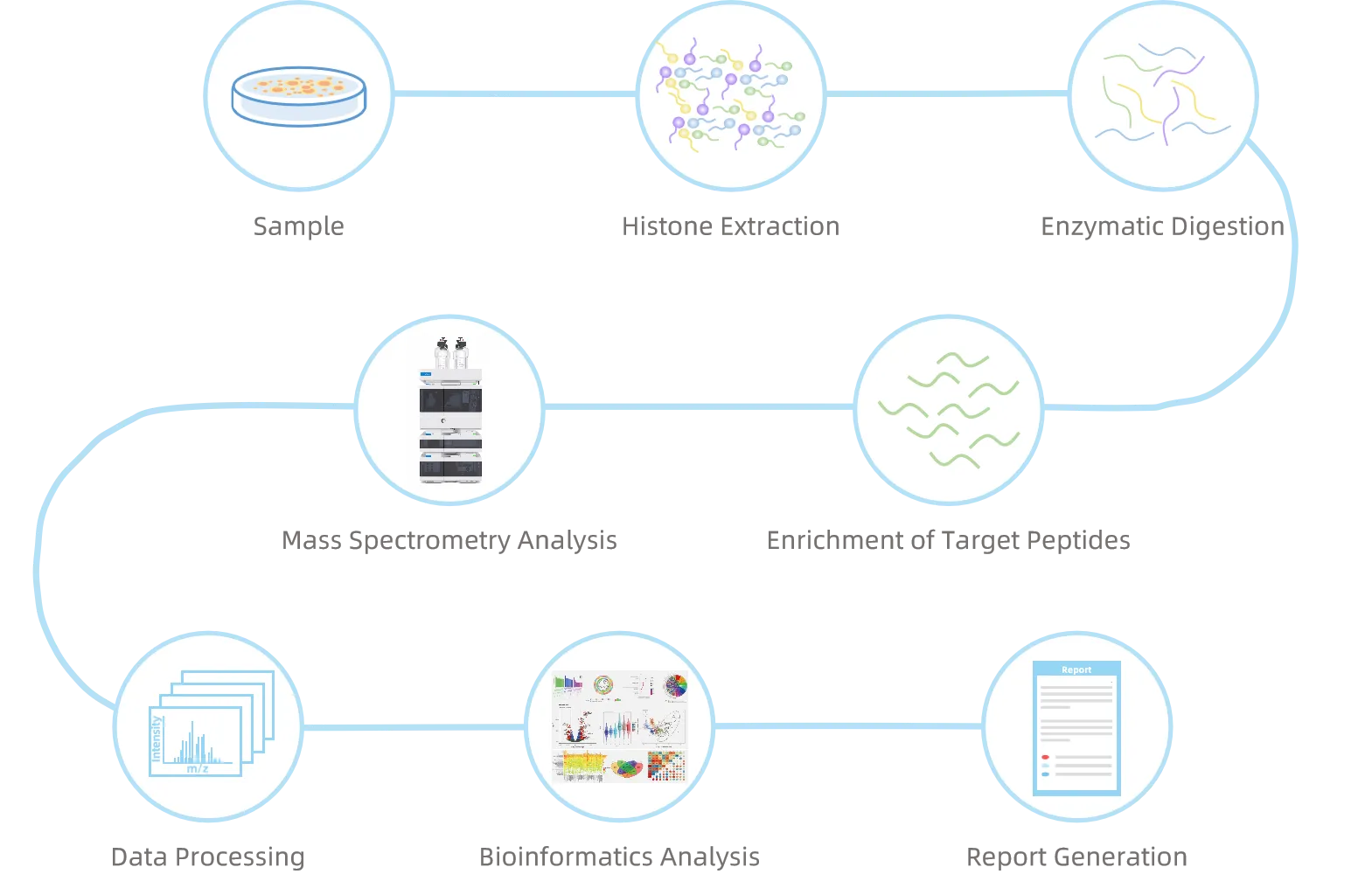
Figure 2. The Workflow of Histone 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Analysis.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types and Quantity
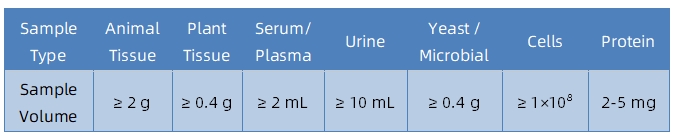
Note: Plasma should be collected using EDTA as an anticoagulant. Standard tissue or cell lysis buffers can be used during protein extraction.
2. Sample Quality
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to maintain protein and modification integrity. Storage at -80°C is recommended.
3. Sample Transportation
Dry ice shipping is recommended to ensure low-temperature conditions throughout transport and minimize the risk of modification loss.
Note: For special samples or customized submission plans, please contact MtoZ Biolabs technical staff in advance.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution Detection
Relying on advanced mass spectrometry platforms, low-abundance 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation modification sites are accurately captured.
2. Specific Enrichment
Optimized peptide enrichment strategies effectively improve modification identification rates and coverage.
3. One-Stop Support
From sample processing to data analysis, comprehensive solutions are provided to ensure efficient research progress.
4. Customized Solutions
Experimental workflows are flexibly tailored according to sample characteristics and research objectives to meet diverse research needs.
Applications
1. Epigenetics Research
Analyze the role of 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation in chromatin remodeling and gene expression regulation.
2. Cell Cycle and Developmental Research
Histone 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation analysis service can be applied to monitor the dynamic changes of this modification during cell division, differentiation, and development.
3. Biomarker Discovery
Systematic detection enables the identification of Khib modifications associated with specific states, supporting potential biomarker screening.
4. Signal Pathway Analysis
Histone 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation analysis service can be used to reveal the regulatory mechanisms of Khib modifications on key signaling molecules and pathway activities.
FAQ
Q1: What Distinguishes Histone 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation (Khib) from Other Lysine Modifications?
A1: Khib is a newly identified lysine post-translational modification. Structurally, it carries a hydroxyisobutyryl group, which is larger and more polar compared with acetylation and methylation. This feature can significantly alter the spatial conformation and charge distribution of histones, thereby exerting unique effects on chromatin state and gene regulation.
Q2: Can It Be Studied in Combination with Other Post-Translational Modifications?
A2: Yes. Khib often acts in concert with modifications such as acetylation and methylation. Combined analysis helps reveal the interplay among multiple modifications and the complexity of their regulatory mechanisms.







