Histone Phosphorylation Analysis Service
Based on the high-resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) platform, the histone phosphorylation analysis service launched by MtoZ Biolabs enables precise detection and quantitative analysis of phosphorylation modifications on histones. Through optimized sample preparation, specific enrichment, and highly sensitive mass spectrometric detection, this service achieves high-confidence identification of low-abundance phosphorylation sites. Combined with bioinformatics analysis, it provides data on modification site distribution, abundance variation, and functional annotation, offering reliable support for studies of chromatin dynamic regulation and signal transduction mechanisms.
Overview
Histone phosphorylation refers to a type of post-translational modification (PTM) in which phosphate groups are covalently attached to serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues of histones, thereby altering histone charge and conformation to influence chromatin compaction and gene expression. This modification plays an essential role in biological processes such as DNA damage repair, chromatin remodeling, cell cycle regulation, and signal transduction. Histone phosphorylation analysis is widely applied in epigenetic research, signal pathway elucidation, and cellular stress response studies, providing key insights into the dynamic regulation of chromatin.
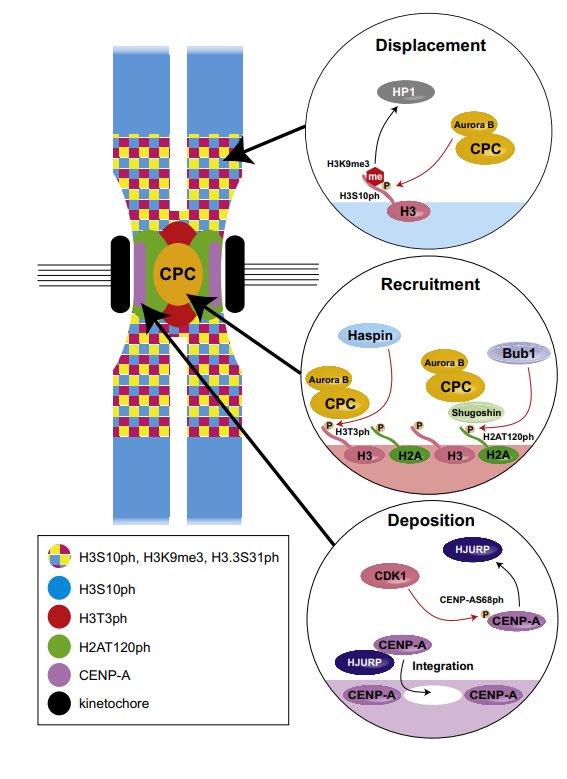
Watson, N.A. et al. Chromatin Signaling and Diseases, 2016.
Figure 1. Histone Phosphorylation Functions during Cell Division.
Analysis Workflow
1. Histone Extraction and Digestion
Histones are extracted from samples and enzymatically digested under optimized conditions to generate detectable peptide fragments.
2. Phosphopeptide Enrichment
Specific enrichment strategies are employed to capture phosphorylated peptides, improving detection sensitivity and coverage.
3. LC-MS/MS Detection
High-resolution mass spectrometry is used for precise identification and quantitative analysis of phosphorylation sites.
4. Data Analysis
Bioinformatics tools are applied to deliver results on modification distribution, abundance variation, and functional annotation, followed by a comprehensive analytical report.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type and Quantity
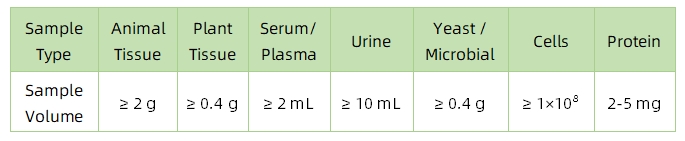
Note: Plasma should be collected using EDTA as an anticoagulant. Standard tissue or cell lysis buffers can be used during protein extraction.
2. Sample Transportation
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Samples are recommended to be stored at -80°C and transported on dry ice to ensure low-temperature conditions throughout the process and prevent modification loss.
Note: For special samples or if a detailed submission plan is required, please contact MtoZ Biolabs technical staff in advance.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution Detection
Leveraging an advanced LC-MS/MS platform, low-abundance phosphorylation modifications are accurately identified and quantified with high sensitivity.
2. Efficient Enrichment System
Optimized strategies such as IMAC or TiO₂ enrichment are employed to effectively capture phosphorylated peptides and enhance detection coverage.
3. Customized Experimental Design
Experimental workflows are flexibly tailored according to research objectives and sample characteristics to meet diverse analytical needs.
4. One-Stop Service
Comprehensive end-to-end support is provided, covering the entire process from sample preparation to data interpretation.
Applications
1. Epigenetic Regulation Studies
Histone phosphorylation analysis service can be used to investigate the role of phosphorylation in chromatin conformation modulation and gene transcription regulation.
2. Cell Cycle Research
By detecting phosphorylation at specific histone sites involved in cell division and cycle regulation, researchers can explore dynamic phosphorylation patterns.
3. Development and Differentiation Research
Histone phosphorylation analysis service enables monitoring of spatial and temporal changes in phosphorylation during cell development and differentiation.
4. Potential Biomarker Discovery
By identifying specific phosphorylation signatures, this service supports the discovery of novel functional biomarkers.
FAQ
Q1: Which Histone Phosphorylation Sites Can Be Analyzed?
A1: This service can detect phosphorylation modifications on multiple histone subtypes (such as H2A, H2B, H3, and H4), including common sites like H3S10ph, H3T3ph, and H2AXS139ph. The detection range can be expanded according to specific research requirements.
Q2: How Does Phosphorylation Analysis Differ from Other PTM Detection Methods?
A2: Phosphorylation involves significant changes in protein charge and exhibits transient signaling characteristics. Its detection requires high-sensitivity mass spectrometry combined with specific enrichment strategies, differing from more stable modifications such as acetylation or methylation.







