MOAC-Based Modified Peptide Enrichment Service
Metal Oxide Affinity Chromatography (MOAC) is a powerful approach for the selective enrichment of phosphorylated and other metal-binding post-translationally modified peptides. By leveraging the affinity between metal oxides and phosphate or carboxyl groups, MOAC enables the efficient isolation of modified peptides from complex biological samples. This method plays a crucial role in modern proteomics, allowing the sensitive detection of low-abundance modifications that regulate signaling, metabolism, and cellular responses.
MtoZ Biolabs provides a professional MOAC-Based Modified Peptide Enrichment Service designed to deliver high-efficiency, reproducible, and quantitative enrichment of modified peptides for downstream mass spectrometry analysis. The MOAC-Based Modified Peptide Enrichment Service integrates advanced titanium dioxide (TiO2) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3) enrichment chemistries with high-resolution LC-MS/MS, enabling precise identification and quantification of phosphorylation, sulfation, and carboxylation events. For optimal coverage, we combine MOAC with complementary strategies such as IMAC, HILIC, or SAX/SCX chromatography, depending on the sample type and target modification. Our team ensures customized experimental designs that adapt to your biological questions, from single protein targets to proteome-scale modification profiling.
Technical Principles
Metal Oxide Affinity Chromatography (MOAC) is based on the strong interaction between metal oxides and phosphate, carboxyl, or hydroxyl groups on modified peptides. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) and zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) are commonly used due to their high selectivity and stability under acidic and organic solvent conditions. The mechanism primarily involves Lewis acid-base interactions, where metal centers act as electron acceptors and interact with electron-donating oxygens of phosphoryl or carboxyl groups.
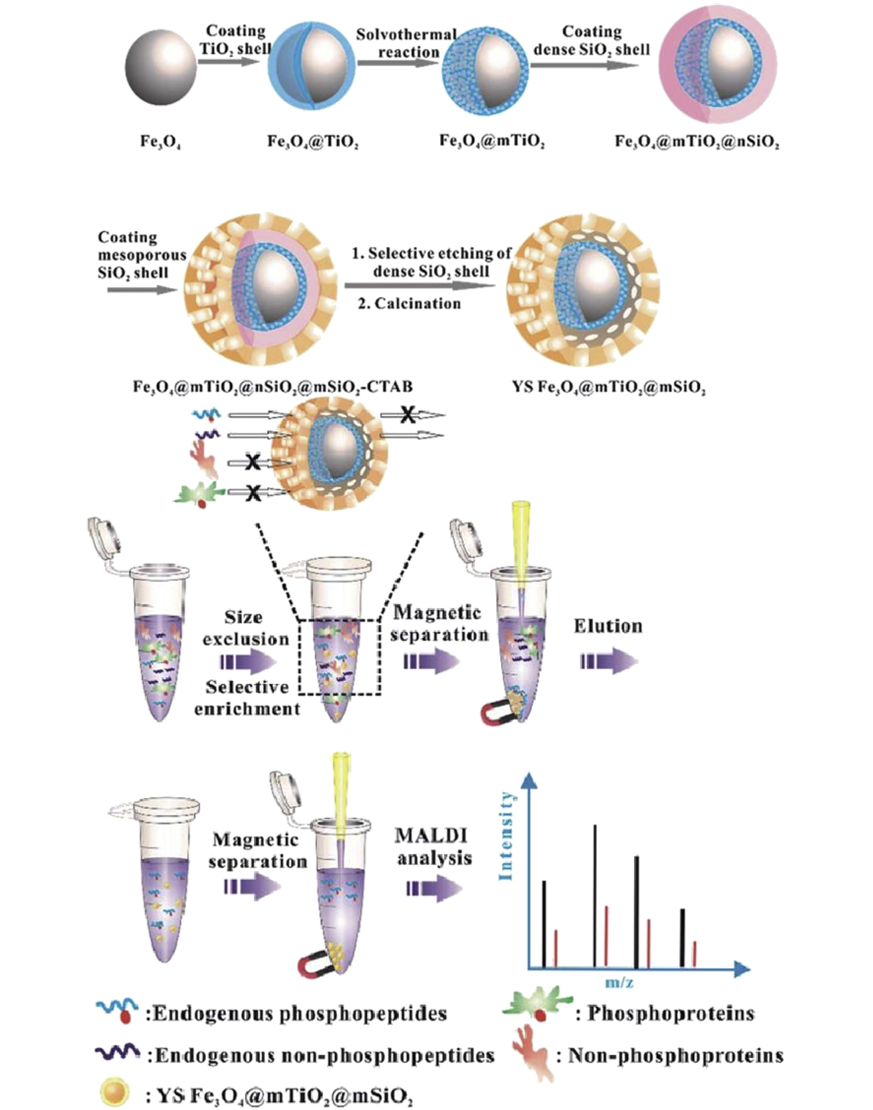
Figure 1. Synthetic Route of Fe3O4@mTiO2@mSiO2 Microspheres and the Procedure of Phosphopeptides Enrichment
This technique has proven indispensable in phosphoproteomics, as phosphorylation typically occurs at low stoichiometric levels. By selectively enriching phosphorylated peptides, MOAC enhances detection sensitivity and improves the depth of proteome coverage. Furthermore, MOAC is applicable to other negatively charged modifications such as sulfation, carboxylation, and glycosylation-related oxidation products, providing a versatile tool for multi-PTM studies.
Analysis Workflow
1. Protein Extraction and Digestion
Proteins from cells, tissues, or biofluids are extracted, denatured, and digested into peptides using optimized conditions to preserve labile modifications.
2. Modified Peptide Enrichment
Peptides are incubated with TiO2 or ZrO2 beads under controlled pH conditions to selectively capture modified peptides while minimizing nonspecific binding.
3. Washing and Elution
Unmodified peptides are removed through sequential washing buffers, and modified peptides are eluted using alkaline or phosphate-based buffers.
4. LC-MS/MS Analysis
Enriched peptides are analyzed using high-resolution LC-MS/MS systems to identify modification sites and quantify their abundance across samples.
5. Data Processing and Interpretation
Bioinformatics analysis includes database searches, PTM site annotation, and pathway mapping to link modification events to biological processes and regulatory networks.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type: Cell lysates, tissue extracts, serum/plasma, or purified protein samples.
2. Amount Required: Minimum 100 µg of total protein per sample for optimal enrichment efficiency.
3. Storage and Transport: Samples should be snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and shipped on dry ice.
4. Buffer Considerations: Avoid high concentrations of phosphate or chelating agents that may interfere with metal oxide binding.
*Note: For specialized sample types or limited material, please contact MtoZ Biolabs before submission for tailored preparation advice.
Service Advantages
✅ High selectivity and reproducibility for phosphopeptide and acidic modification enrichment.
✅ Optimized workflow offering enhanced sensitivity and reduced processing time.
✅ Flexible enrichment protocols adaptable to various sample types and modification targets.
✅ Skilled technical team ensuring reliable data interpretation and strong experimental support.
✅ Tailored strategies designed to meet specific project goals and research applications.
Applications
1. Phosphoproteomics Research
Enables large-scale profiling of phosphorylation events to study kinase activity and signaling regulation.
2. Signal Transduction Studies
Supports mapping of dynamic phosphorylation networks involved in cellular communication and stress responses.
3. Protein Function Analysis
Facilitates investigation of modification-dependent protein activation, localization, and interaction mechanisms.
4. Disease Mechanism Research
Applied in studying abnormal phosphorylation patterns in cancer, neurodegeneration, and cardiovascular diseases.
5. Drug Development and Target Validation
Assists in identifying PTM-related drug targets and evaluating treatment-induced signaling changes.
6. Biomarker Discovery
Helps uncover phospho-based biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic monitoring.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment (project-dependent)
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation (project-dependent)
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
MtoZ Biolabs' MOAC-Based Modified Peptide Enrichment Service provides a powerful and versatile solution for exploring phosphorylation and other negatively charged modifications with high specificity and sensitivity. Whether for targeted studies or large-scale PTM discovery, our comprehensive platform delivers reliable, publication-ready results that accelerate scientific discovery and innovation. Contact us today to discuss your project and request a customized proposal!







