Protein N-glycosylation Profiling Service
MtoZ Biolabs, leveraging advanced chromatography and mass spectrometry platforms, provides Protein N-glycosylation Profiling Service that covers the complete workflow from sample preparation and N-glycan release and enrichment to high-sensitivity mass spectrometry detection and in-depth data analysis. Our service includes:
-
N-glycan Structure Analysis: Accurate characterization of glycan composition, sequence, linkage type, and structural isomers.
-
Glycosylation Site Identification: Determination of N-glycan modification sites on proteins and their occupancy levels.
-
Quantitative Analysis: Comparison of N-glycan abundance changes under different conditions using either label-free or labeling approaches.
-
Customized Solutions: Tailored analytical strategies designed to meet the diverse needs of drug development, disease research, and biomarker discovery.
Overview
Protein N-glycosylation is one of the most common post-translational modifications, occurring in approximately 50 percent of proteins in eukaryotic cells. It involves the attachment of oligosaccharides to the conserved sequence N-X-(S/T) (where X ≠ P), regulating protein folding, stability, and biological functions. N-glycosylation plays a critical role in cell adhesion, immune response, signal transduction, and disease development. Common types of N-glycans include high-mannose, complex/hybrid, sialylated, fucosylated, xylosylated, and mannose-6-phosphate (M6P) glycans.
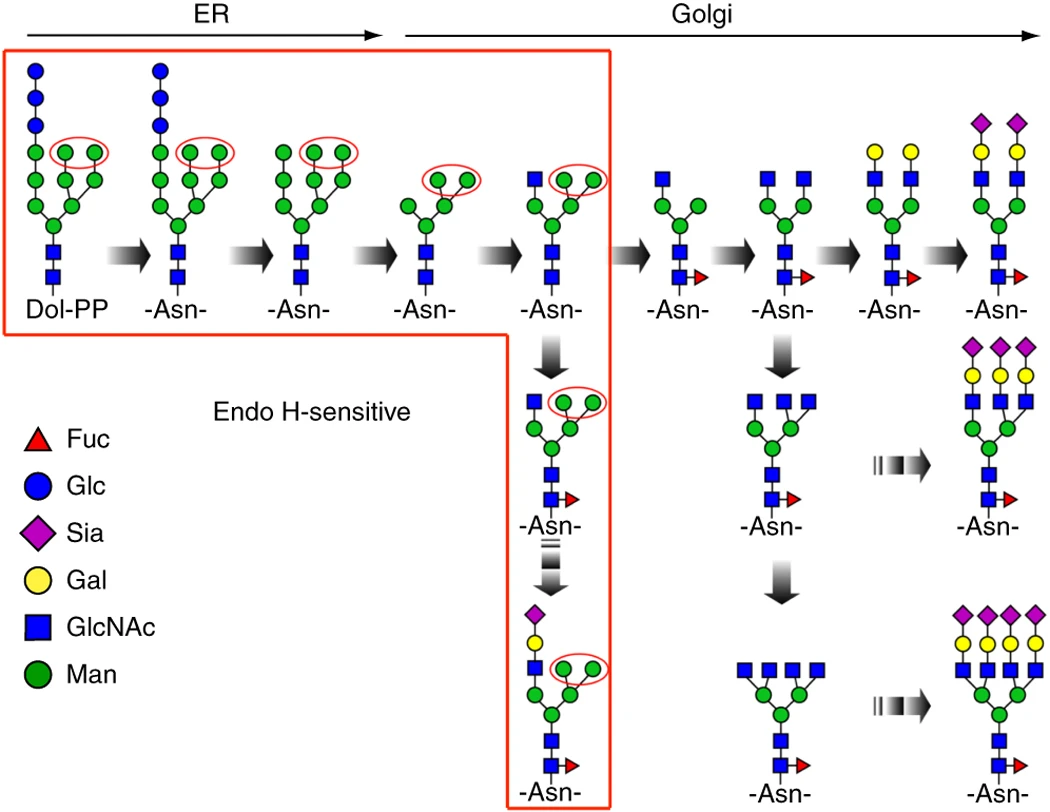
Cao L. et al. Nat Protoc. 2018.
Figure 1. N-linked glycan processing in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus.
Technical Principles
Protein N-glycosylation Profiling Service is typically performed using high-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) platforms. The process begins with the release of N-glycans from proteins using specific glycosidases such as PNGase F, followed by purification and enrichment through solid-phase extraction, HILIC chromatography, or lectin affinity methods to remove contaminating peptides and unmodified proteins. The separated glycans can then be derivatized with fluorescent or isotopic labels to enhance detection sensitivity and improve quantitative accuracy.
In the mass spectrometry stage, MALDI-TOF MS or LC-MS/MS is commonly employed to resolve glycan composition, sequence, linkage type, and structural isomers. Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) provides additional detail for precise structural elucidation of glycans. On the data analysis side, glycan databases and bioinformatics algorithms are used to identify and quantify glycan types and abundance under different sample conditions. This approach enables multilayered analysis ranging from glycosylation sites to complete N-glycan structures, providing systematic data support for disease mechanism studies, biomarker discovery, and biopharmaceutical development.
Service Advantages
1. High Resolution and Sensitivity
Capable of detecting low-abundance N-glycans and resolving highly complex glycan structures.
2. Comprehensive Analysis
Covers glycan-level, glycopeptide-level, and whole-protein-level characterization, with complementary results across different layers.
3. Advanced Enrichment and Purification Methods
Combines lectin affinity, HILIC chromatography, and derivatization labeling strategies to significantly enhance coverage and quantitative accuracy of target N-glycans.
4. Strong Quantitative Capability
Supports both label-free and multiple labeling strategies, enabling reliable comparative quantification.
Sample Submission Suggestions
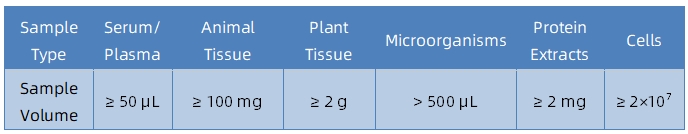
It is recommended to contact our technical support team before submitting samples to confirm their suitability and to receive tailored submission guidance.
Applications
1. Pharmaceutical Development
Monitor the impact of glycan patterns on the stability and efficacy of biopharmaceuticals, supporting quality control in biologics manufacturing.
2. Disease Research
Characterize disease-associated glycosylation changes to identify and evaluate potential biomarker candidates.
3. Immunology Research
Investigate mechanisms of immune cell differentiation and receptor-ligand interactions mediated by glycosylation.
4. Functional Studies
Elucidate the roles of glycans in protein folding, localization, and signal transduction.
FAQ
Q1: Can Protein N-glycosylation Profiling Service Distinguish Glycan Isomers (Such as Different Sialic Acid Linkages)?
A1: Yes. With high-resolution LC-MS/MS combined with MS/MS fragmentation data, it is possible to distinguish common isomeric forms, such as α2,3 and α2,6 sialic acid linkages. If needed, orthogonal separation techniques such as UPLC-HILIC can be employed to further improve resolution.
Q2: How Is Quantitative Analysis Achieved? Does It Support Absolute Quantification?
A2: We offer both label-free and stable isotope/chemical labeling strategies. Label-free approaches are suitable for large-scale relative quantification, while isotope labeling methods such as TMT and iTRAQ enhance quantitative accuracy across samples. Absolute quantification typically requires the use of glycan standards or internal standards.







